Over the last decade, the tech industry has become accustomed to the term hyperscale as the backbone of cloud computing. However, the explosion of generative artificial intelligence has forced this industry to evolve faster than expected. We are now leaving the era of conventional data centers and entering the “Mega-Hyperscale” phase, often referred to as the AI Superfactory.
The main difference lies in energy density and workload characteristics. While traditional cloud serves millions of separate, small requests, AI requires hundreds of thousands of chips working simultaneously as one giant brain. This fundamentally changes how these facilities are built and operated.
By definition, an AI Superfactory is a data center facility designed specifically to train a single massive artificial intelligence model, rather than just storing data or running web applications.
Unlike traditional cloud data centers consisting of thousands of independent servers, an AI Superfactory connects tens to hundreds of thousands of graphics processing units (GPUs) into one giant computing cluster. In this facility, the entire building functions like a single supercomputer. The goal is to minimize data latency between chips and maximize power efficiency for intensive machine learning processes.
To understand this massive scale, we can look at what is happening with the world’s largest tech players today. Training a single cutting-edge AI model now requires facilities built with unprecedented speed and capacity.
For example, xAI’s “Colossus” supercomputer facility in Memphis was built in just 122 days to house 100,000 GPUs, which is now expanding towards 200,000 units. This scale creates such a huge and sudden energy demand that developers had to use independent power generation because the local grid could not supply the additional power instantly.
On the other hand, the main obstacle for the industry right now is no longer chip availability, but rather power socket availability. A Microsoft executive even revealed that they have thousands of sophisticated GPUs sitting in warehouses because there isn’t enough power capacity ready to turn them on. This proves that in the AI era, electric power is the most valuable commodity.
Previously, facilities with a capacity of 30 to 50 Megawatts (MW) were considered large hyperscale campuses. However, due to the energy-hungry needs of AI training, the definition of “large” has shifted drastically. Modern facilities are now designed with targets of hundreds of Megawatts up to Gigawatt scale in a single campus location.
This shift in standards is happening globally, including in Asia. Infrastructure providers are now racing to build jumbo capacity to accommodate the wave of regional AI demand. As an illustration, Digital Edge DC is actively developing facilities with capacities above 100MW to 300MW in several countries such as South Korea, India, Indonesia, and Thailand. Readiness to provide infrastructure on the scale of hundreds of megawatts has now become an absolute requirement for data center players who want to remain relevant in the global market.
The shift to the “AI Superfactory” also fundamentally changes the technical specifications inside the building. Traditional server racks for web applications usually consume only 5-10kW of power. Conversely, modern AI racks containing the latest generation chips like NVIDIA Blackwell can consume more than 100kW per rack.
The implications for cooling systems are enormous. Conventional air conditioning (AC) is no longer adequate to handle the heat generated by such high density. Future facilities must now adopt liquid cooling technology directed straight to the chip to maintain optimal computing performance.
The direction of data center development is very clear. We are transitioning from mere data storage facilities to digital intelligence generation facilities. In this Mega-Hyperscale era, data centers are no longer viewed just by their building square footage, but by how large and reliable their power supply is. The winners in this AI race will not be those who just have the best algorithms, but those who possess the most robust physical infrastructure to run them.
2026 Data Center Trend Forecast Series – Part 3 of 4
The year 2026 is no longer just about buildings filled with servers. We are witnessing a total transformation in cooling architecture. The industry’s focus is shifting from merely Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) to Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE). This article will discuss how new technologies are breaking the myth that AI must always be water-intensive, especially in tropical climates.
Throughout 2024 and 2025, media narratives often highlighted how water-intensive AI is. Headlines frequently stated that “one chatbot conversation is equivalent to wasting a bottle of water.” However, it’s important to understand the physics behind these claims.
In conventional data center designs, heat is dissipated through cooling towers. These systems work by evaporating water into the atmosphere to remove heat. In this old model, the harder chips work (to train AI models), the more heat is generated, and the more water has to be evaporated. A report from researchers at the University of California estimated that training GPT-3 alone consumed thousands of liters of water.
However, in 2026, this linear correlation between “high performance” and “water waste” is starting to break. The data center industry is moving away from open evaporation methods in favor of much more sophisticated closed-loop technologies. Used water is not discarded but recycled for reuse.
The shift to the Asia Pacific region (as discussed in Part 2) brings its own technical challenges. Countries like Indonesia, Singapore, and the Philippines have very high levels of air humidity.
Traditional evaporative cooling systems work very inefficiently in tropical areas. You cannot effectively cool water by evaporating it into air that is already saturated with water (humid). As a result, data center operators often have to expend more energy and water just to keep server temperatures stable.
This is what is driving the birth of a new standard in 2026: Membrane Technology.
To overcome the “heat trap” in tropical regions without depleting local groundwater reserves, new technologies such as liquid cooling systems are becoming standard for forward-thinking operators.
Unlike traditional cooling towers that spray water into the air, these systems use semi-permeable membranes—imagine a giant Gore-Tex layer for data centers. This technology separates water from the airflow. The membrane allows heat to escape through microscopic water vapor but retains liquid water to prevent it from being wasted and prevents contaminants from outside air from entering the system.
The results are very significant for the 2026 sustainability trend:
The implementation of this technology is no longer just theory. Regional digital infrastructure companies like Digital Edge have begun implementing liquid cooling technology in their facilities, such as in Indonesia and the Philippines, to prove that high density can be achieved in tropical climates without sacrificing water efficiency. This is a real example of how physical innovation enables AI expansion in areas previously considered too hot or humid.
In 2026, hyperscale clients (giant technology companies) will no longer just ask, “What is your electrical capacity?” but also “What is your WUE number?”
Water Usage Effectiveness (WUE) is becoming as important a metric as PUE. In many countries, permits for new data center construction are increasingly restricted regarding groundwater use, especially as data centers often compete with the clean water needs of surrounding communities.
The data center architecture of the future will be “hybrid.” On the roof, membrane systems (such as liquid cooling) create a closed cold-water cycle. Inside the server room (data hall), this cold water is directed to two destinations:
This combination allows data centers to handle very heavy AI workloads with a near-zero water footprint.
The physical transformation of data centers in 2026 is about becoming “environmentally invisible,” so that data centers will not affect their surrounding environment. The main trend is to decouple computing growth from natural resource consumption.
The future of AI infrastructure is not about finding more water to dissipate into the atmosphere, but rather engineering systems so that such waste is eliminated entirely. With the adoption of membrane-based cooling technology and liquid cooling, data centers in 2026 will be quiet, cool, and water-efficient utilities, ready to support the global artificial intelligence revolution.
2026 Data Center Trend Forecast Series – Part 2 of 4
The Asia-Pacific region is currently experiencing an unprecedented digital infrastructure transformation. This region is estimated to contribute approximately 30% of global capacity expansion over the next five years, with total investment reaching over $564 billion by 2028. This massive capital injection is transforming various aspects, from cloud computing to artificial intelligence (AI) deployment. While legacy hubs like Singapore and Tokyo face power constraints and land scarcity, a new class of emerging markets is starting to stand out—creating opportunities that were unavailable just a few months ago.
Several converging forces are making 2026 a turning point for digital infrastructure across the region.
The generative artificial intelligence revolution continues. Modern AI workloads require specialized high-density racks and advanced cooling systems. The industry notes an increase in average server rack power density, with wider adoption in the 10 kW to 30 kW range; however, facilities exceeding 30 kW are still relatively few, and facilities with very high density are still rarely encountered, as noted in the Uptime Institute’s 2025 Global Data Center Survey. This density increase creates urgent demand for new AI-ready facilities.
Governments across Southeast Asia are enforcing stricter data residency requirements. Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia have introduced regulations requiring financial and personal data to remain within national borders. This compliance-driven surge requires companies to no longer route all processes through a single hub like Singapore—they must build local facilities in various jurisdictions simultaneously.
Various capital owners (retail, private, and state) have assessed data centers as valuable portfolio assets. The market has provided unprecedented capital, enabling rapid development. The overall Asia-Pacific data center market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.40% from 2025 to 2035, driven by these billion-dollar joint ventures.
Discussions surrounding APAC data center expansion always return to the issue of power—but the narrative has shifted from “cheap power” to “available and sustainable power.”
Goldman Sachs estimates that global power demand from data centers will increase by 50% by 2027 and is projected to rise up to 165% by 2030 compared to 2023 levels. In established markets, this condition creates power grid bottlenecks. Singapore’s recent moratorium (now lifted with strict sustainability requirements) forced operators to seek alternative locations. Tokyo faces similar constraints, where some developers must wait 3-5 years for power grid connections.
Asia is home to 83% of the world’s coal-fired power plants, yet clean energy investment has now significantly surpassed fossil fuel investment in the region. The total combined share of renewable energy in Asia reached 29% in 2024. Hyperscalers demand Power Purchase Agreements that encompass renewable energy. And providers who can supply pure green power command a price premium—even in markets where coal still dominates the grid mix.
Read more: Driving the Future: Integrating Renewable Energy into Data Centers
Although air cooling remains the baseline standard for most facilities, the need to support extreme density AI clusters (generally over 30 kW per rack) is driving the adoption of immersive and direct-to-chip cooling as baseline specifications for newly built facilities. This reflects emerging hardware demands in the market.
Instead of immediately establishing 100MW mega campuses, operators are building in phases of 10-20MW that can be operational within 12-18 months. This approach aligns with customer demand, providing flexibility in expansion. This approach dominates in emerging markets like Indonesia, where demand is strong but gradual.
Read more: The Future of Data Center Indonesia: Infrastructure and Investment on the Rise
The role of data centers in APAC is shifting from the traditional leased space model to interconnection hubs. The presence of carrier-neutral facilities with rich ecosystems (including the financial services industry, enterprises, ISPs, etc.) creates network effects that underpin premium pricing. This model becomes a valuable asset, especially in regions where international bandwidth capacity is skyrocketing, but local exchange infrastructure is still relatively minimal.
For companies planning 2026 deployments, strategic considerations are becoming complex. Hyperscalers are launching new availability zones across APAC on an unprecedented scale, but site selection now involves evaluating dozens of variables beyond just connectivity.
Power availability is the top priority—is 50 MW capacity available now with potential scalability up to 200 MW? Renewable energy supply becomes the next crucial consideration, given that many RFPs now require 100% green energy from the start of operations. Other important factors include fiber optic diversity, earthquake risk, flood-prone areas, and local regulatory stability.
This is where regional specialists add value. Companies like Digital Edge, with operations hubs in APAC, possess what global operators struggle to offer: an understanding of regional standards and local expertise. Especially regarding bureaucracy, land, and power capable of supporting hyperscale performance or larger. Regional operator facilities have been optimized for tropical climates; and distributed layouts to reduce environmental/natural disaster risks while remaining close to best connectivity routes.
This advantage is not just operational—but also temporal. In markets where securing land and power can take 18-24 months, working with a provider who has completed the groundwork can accelerate deployment by a year or more.
The APAC data center narrative is not just about capacity—but about capability. By 2026, this region will transition from follower to leader in defining next-generation data center architecture. Markets across Southeast Asia are leapfrogging legacy constraints to deliver AI-ready, sustainably powered, and hyper-connected infrastructure.
For companies planning their 2026 digital strategies, the message is clear: the emerging APAC market is no longer a secondary option, but a primary deployment destination. The question is no longer whether to build a presence, but how quickly capacity can be secured before this fast-growing market tightens. The expansion isn’t coming—it is already happening.
2026 Data Center Trend Forecast Series – Part 1 of 4
As 2026 draws near, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to transform the global data center landscape at an unprecedented pace. In this four-part series, we explore the core trends defining the industry’s next chapter. This first installment examines how AI is reshaping data center infrastructure and technology—from surging power demands and hyperscale evolution to cooling innovations and even space-based data centers.
Read also: Understanding AI Data Centers: Key Specifications and Hardware
AI workloads demand vastly more computing power than traditional applications, largely due to the use of GPUs and high-performance accelerator servers. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global data center electricity consumption is projected to approach 1,050 terawatt-hours (TWh) by 2026—making data centers the fifth-largest electricity consumer worldwide.
In recent years, AI has accounted for roughly 5–15% of total data center power use, a figure that could rise to 35–50% by 2030 under high-growth scenarios. In the U.S. alone, data centers consumed around 4% of national electricity in 2024, with demand expected to more than double by 2030—driven primarily by the AI boom.
Research from MIT News suggests that AI-optimized data centers could require up to 90 TWh of electricity annually by 2026. More strikingly, an analysis from MIT Sloan found that global AI data centers might consume as much as 21% of the world’s total energy if the delivery of AI services to end users is included. These factors are propelling the rise of hyperscale data centers—massive facilities capable of handling hundreds of megawatts to power AI’s exponential growth.
AI isn’t just consuming more power—it’s redefining the structure of the modern data center. Deloitte projects that power demand from AI data centers in the U.S. could grow more than thirtyfold to 123 gigawatts (GW) by 2035, fueling the next generation of modular, flexible hyperscale designs.
Tech giants such as Alphabet, Amazon, Microsoft, and Meta are at the forefront of this wave, investing more than US$350 billion in data center construction this year and up to US$400 billion by 2026. These hyperscale sites are built to manage massive AI workloads—particularly for training and deploying large language models. Structure Research predicts that by 2026, hyperscale facilities will form the backbone of global cloud and edge computing infrastructure, supporting rapid AI-driven expansion.
Architecturally, composable infrastructures are also on the rise, allowing resources like GPUs to be dynamically allocated across workloads for optimal efficiency. In Indonesia, providers like EDGE DC are following this global trend, developing hyperscale facilities equipped for scalable AI operations backed by advanced technologies.
The industry’s energy transformation is still underway. Today, most data centers draw power from national grids that remain heavily reliant on fossil fuels. The IEA estimates that coal and natural gas will supply more than 40% of additional electricity demand from data centers through 2030.
Nonetheless, renewable sources—solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal—are rapidly gaining appeal. In the U.S., home to more than 5,400 data centers as of March 2025, clean energy adoption has become a strategic priority. In Indonesia, EDGE DC is leading by example through its use of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) from state utility PLN, sourced from geothermal power.
As rack power density rises beyond 100 kW per rack in AI environments, traditional air cooling can no longer keep up. Liquid cooling technologies—such as direct-to-chip and immersion systems—are emerging as the new standard, offering energy efficiency improvements of 30–50%.
Industry leaders including Schneider Electric, Vertiv, and LiquidStack are driving innovation in this space. Across the Asia-Pacific region, adoption of advanced cooling methods is accelerating. EDGE DC, for example, implemented Nortek’s StatePoint® Liquid Cooling System at its 23 MW EDGE2 facility—making it Indonesia’s first data center to use indirect evaporative cooling with a semi-permeable membrane. The system dramatically reduces both electricity and water consumption and performs well in hot, humid tropical climates.
Hybrid liquid cooling can also cut water usage by as much as 90% in arid regions—an essential advantage where water scarcity is a serious issue.
Read also: How Generative AI Is Transforming Data Centers
As AI demand skyrockets, engineers are looking beyond the planet for solutions. Google’s Project Suncatcher is exploring the concept of space-based AI infrastructure, deploying TPU chips in orbit to harness limitless solar energy and escape the constraints of terrestrial power and space.
Developed in collaboration with Planet Labs, the project aims to launch its first test hardware in early 2027. The design envisions a constellation of 81 interconnected satellites linked by optical communication channels, forming a kilometer-long computing array. This visionary initiative could reduce energy costs up to tenfold compared to ground-based data centers—though challenges such as cooling in a vacuum and communication delays must still be solved.
AI is propelling data center innovation to new heights—powering the growth of ever-larger hyperscale facilities, smarter cooling systems, and bold new frontiers like orbital computing.
For data center operators, the path forward lies in hyperscale scalability, adoption of cutting-edge technologies, and exploration of unconventional locations. As AI continues to dominate digital infrastructure by 2026, the combination of explosive growth and relentless innovation will define a stronger, more resilient, and adaptive global data ecosystem.
The infrastructure initiative called Candle Project was recently introduced to the public. This project aims to build the largest-capacity undersea cable system in the Asia Pacific (APAC) region.
The cable will connect Japan, Taiwan, the Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore—spanning a total distance of 8,000 kilometers with a data transfer capacity of up to 570 terabits per second (Tbps).
Scheduled to be operational in 2028, the Candle Project marks a major milestone in the global expansion of digital infrastructure, strengthening the foundation of internet connectivity and AI-based services across one of the fastest-growing digital economies in the world.
Asia Pacific is currently home to more than 58% of global internet users. With the increasing reliance on digital services, demand for high-capacity and low-latency networks has become essential.
Through the Candle Project, along with the Bifrost, Echo, and Apricot cable systems, the region will secure reliable and efficient intercontinental data capacity.
Together, these four subsea cable systems will become the backbone of Asia Pacific’s digital connectivity to the Americas and beyond.
The Candle Project is not merely a telecommunications investment; it also carries significant implications for the growth of the data center industry in Southeast Asia.
This large-scale capacity and regional connectivity will result in:
As a data center provider focused on reliability, energy efficiency, and high connectivity, EDGE DC sees projects like Candle as strategic opportunities to expand local data ecosystems supported by robust global infrastructure.
Investments in projects like Candle, Bifrost, Echo, and Apricot are part of a long-term commitment to building a resilient, high-capacity global digital network.
This initiative aligns with the broader vision of providing wider access to AI-based and emerging technologies for billions of internet users worldwide.
With enhanced cross-border connectivity, data center operators such as EDGE DC will play a crucial role in ensuring that data flows rapidly, efficiently, and securely—bridging global infrastructure and local end-users.
The Candle Project marks a new chapter in Asia Pacific’s connectivity development. With its hundreds of terabits per second of capacity and multinational reach, the system will strengthen the foundation for digital transformation across the world’s fastest-growing region.
At the same time, the presence of this large-capacity submarine cable will drive the expansion of local data center ecosystems as integral components of the global digital network.
In the midst of the digital transformation wave, internet connectivity is no longer just an accessory, but the backbone of every business’s operations. From disruptive startups to multinational corporations, the reliance on fast, stable, and scalable networks continues to grow. However, behind the seamless access to information we enjoy, a fundamental shift is underway: the transition from IPv4 to IPv6. Understanding the differences and the urgency of this migration is key to ensuring your business remains relevant and competitive in the digital future.
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4), the protocol that has been the foundation of the internet for decades, is based on a 32-bit addressing scheme. This means there are only approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses that can be allocated. At the time of its design, this number was considered more than sufficient. However, the explosive growth of the internet—with billions of smartphones, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, data center servers, and other digital infrastructure—quickly depleted these address reserves.
Since around the early 2010s, regional internet registries (RIRs) worldwide, including those in the Asia Pacific region, have officially announced the exhaustion of IPv4 address supplies. In Indonesia, this scarcity is palpable, forcing many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to extensively use methods like Network Address Translation (NAT). While NAT serves as a temporary solution to allow multiple devices to share a single public IP address, it inherently adds a layer of complexity and can introduce performance challenges.
Read more: IP Peering vs. IP Transit: Which is Right for Your Network?
For modern businesses heavily reliant on digital infrastructure—especially for those utilizing data center colocation services for their critical servers and applications—IPv4 scarcity brings serious consequences:
For EDGE DC and our clients who prioritize high uptime, scalability, and connectivity efficiency, the IPv4 issue is no longer merely a technical concern but a business risk that needs to be mitigated.
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) emerges as a crucial evolution designed to address the limitations of IPv4. With a 128-bit architecture, IPv6 offers an astronomical number of addresses: approximately 3.4 x 1038 unique addresses. This figure ensures that every device on Earth, even every atom in the universe, can have its own IP address, eliminating concerns about scarcity forever.
Beyond the sheer quantity of addresses, IPv6 also brings fundamental improvements that enhance network performance and security:
The global transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is a gradual process, often involving dual-stack implementations where networks support both protocols simultaneously. For businesses and data centers, the success of this transition heavily relies on the support of proactive ISPs.
Premium connectivity providers like CBN, through their CBN Premier Connectivity service, have been at the forefront of providing robust and integrated native IPv6 support. This enables businesses collocating their infrastructure in data centers like EDGE DC to adopt IPv6 seamlessly without compatibility hurdles.
With the right ISP support, EDGE DC clients can:
As a carrier-neutral data center, EDGE DC offers clients the flexibility to choose the most suitable ISP, including providers with strong IPv6 capabilities like CBN. This combination ensures maximum flexibility and resilience in building an adaptive network architecture ready to face every digital dynamic.
Read more: Fundamental Differences: Business vs. Home Fiber Optic Internet
IPv4 scarcity is no longer a future threat—it is an operational reality today. Visionary businesses that proactively adopt an IPv6-ready network strategy will gain a significant competitive edge. They will not only be free from IP address limitations but will also enjoy improved operational efficiency, enhanced security, and a solid foundation for continuous innovation.
When planning your connectivity strategy, it is crucial to choose partners who understand and have comprehensively implemented the IPv6 transition. By partnering with leading network providers like CBN, who are committed to the latest technology standards, and by placing infrastructure in modern data centers like EDGE DC, your company can ensure a strong, secure, and scalable connectivity foundation to support your digital ambitions in the future.
A single second of downtime can mean losing thousands of customers. Imagine an e-commerce site during a flash sale or a banking application on payday; massive traffic spikes can overwhelm servers and eventually crash them. This is the problem load balancing aims to solve.
For developers, system administrators, or business owners, understanding what load balancing is no longer an option but a necessity for building reliable and scalable applications.
This article will thoroughly discuss the concept of what a server load balancer is, ranging from how it works, its types, to simple architecture examples you can implement. Let’s get started.
Simply put, load balancing is the process of distributing network or application traffic evenly across multiple servers behind it. Think of a load balancer as a clever traffic manager at the entrance of a highway with many toll gates. Instead of letting all cars pile up at one gate, this manager directs cars to less busy gates to ensure no long queues and everything runs smoothly.
In the digital world, “cars” are requests from users (like opening a webpage or making a transaction), and “toll gates” are your servers. The load balancer sits between users and your server farm, acting as a single point of entry that then efficiently distributes the workload.
Implementing load balancing provides three key advantages crucial for modern applications:
Read also: Vertical vs Horizontal Scaling: Determining the Direction of Your Infrastructure Scalability
Load balancers do not all work the same way. The main difference lies in the OSI Model layer at which they operate. The two most common types are Layer 4 and Layer 7.
A Layer 4 load balancer operates at the network level. It makes routing decisions based on information from the transport layer, such as source/destination IP addresses and port numbers.
This is a more sophisticated type of load balancer and is commonly used for web app load balancing. It operates at the application layer, meaning it can “read” and understand the content of requests, such as HTTP headers, cookies, and URLs.
To maximize its functionality, a load balancer is supported by several important concepts:
There are many load balancer software options, both open-source and commercial. Here are three of the most popular:
Let’s visualize how all of this works together in a simple architecture:
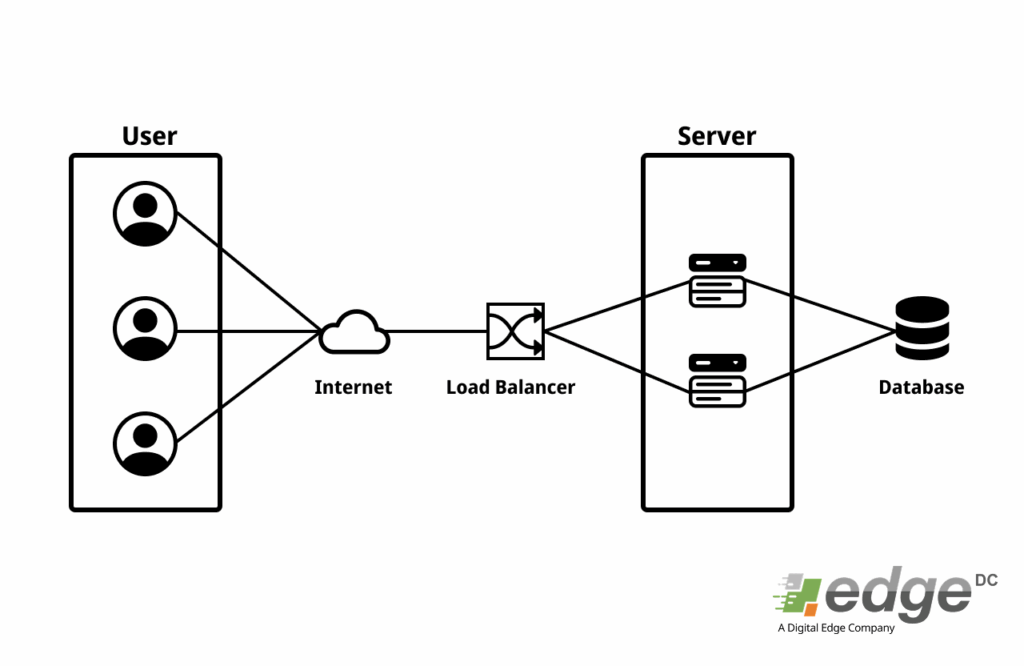
Load balancing is no longer a luxury but a fundamental component in designing robust, fast, and scalable application architectures. By intelligently distributing workloads, it not only maintains application performance at peak levels but also provides a crucial safety net to ensure your services remain operational even when problems occur on one of the servers.
Choosing the right type of load balancer (Layer 4 or Layer 7) and configuring features like health checks and session persistence will be key to the success of your digital infrastructure.
Imagine the application or website you built is used by millions of people. Users are pouring in, traffic is skyrocketing, and the server that used to run smoothly is now starting to feel slow. This is a good problem to have, but it’s also a critical juncture that will determine the future of your product. The answer lies in one word: scalability.
The answer lies in one word: scalability. This scalability is inseparable from the physical infrastructure where your servers run, often located in a data center. However, scalability is not a magic trick. There are two main options that are often debated among developers and DevOps: vertical scaling and horizontal scaling. Choosing the wrong path is not only costly, but can also lead to downtime and degrade the user experience.
This article will thoroughly explore what vertical scaling is, what horizontal scaling is, and a comparison of horizontal vs vertical scaling. The goal is for you to make the right decisions about your infrastructure’s scalability direction.
Vertical scaling is the process of increasing the capacity of an existing server by adding more resources. Imagine you have one very capable chef. When orders pile up, you don’t hire new chefs; instead, you give him sharper knives, a larger stove, and a wider workspace. He remains one person, but is now stronger and faster.
That’s the essence of vertical scaling, also often referred to as scale-up.
Horizontal scaling is the process of adding more servers or instances to distribute the workload. Going back to the chef analogy. Instead of making one chef “super,” you hire more chefs. Each chef works on a portion of the orders, and collectively, they can handle a much larger volume.
This is the core of horizontal scaling, or scale-out. You don’t make one server bigger, but you increase the number of servers.
To simplify, let’s compare both in a table:
| Aspect | Vertical Scaling (Scale-Up) | Horizontal Scaling (Scale-Out) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Concept | Enlarging a single server (adding CPU/RAM). | Adding more servers (adding instances). |
| Scalability Limit | Limited by maximum hardware capacity. | Virtually unlimited, as long as the architecture supports it. |
| Availability | Low. There is a Single Point of Failure. | High. Failure of one node does not bring down the system. |
| Complexity | Low initially, easy to implement. | High, requires load balancer and application design. |
| Cost | High-end hardware costs are very expensive. | More efficient, can use standard hardware. |
| Application Impact | Generally requires no code changes. | Application must be designed for a distributed environment. |
In the modern era, horizontal scaling has become much easier thanks to technologies like containerization and orchestration.
Docker and Kubernetes are key pillars that make horizontal scaling the dominant strategy for modern applications.
There is no “one-size-fits-all” answer. The choice between vertical vs horizontal scaling depends on your needs, architecture, and budget.
In practice, many modern systems use a hybrid approach: applying vertical scaling for certain components that are difficult to distribute (like a primary database) and horizontal scaling for other stateless components (like web application servers).
Scalability planning is an investment. By understanding the fundamental differences between scale-up and scale-out, you can build an infrastructure foundation that is not only strong today but also ready for future growth.
For organizations, especially those with multiple branch offices or teams spread across different regions, having a stable and secure communication network is essential. In this context, Wide Area Network (WAN) technology emerges — a network architecture that allows businesses to connect branch offices, data centers, and even business units in distant locations.
However, as technology evolves, traditional WAN now has a smarter and more flexible successor, namely SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network). To better understand this evolution, let’s first explore WAN: its definition, how it works, types, and the benefits it brings for business.
WAN (Wide Area Network) is a computer network that spans a wide geographical area, designed to connect multiple local area networks (LANs) or metropolitan area networks (MANs) across different locations so they remain integrated.
A simple example is a banking network that connects branch offices across a country with a national data center, or a multinational corporation that integrates operations from various countries.
The main purpose of WAN is to enable communication, data sharing, applications, and network resources between locations without geographical limitations.
WAN works by connecting several LANs or MANs using specific networking devices and communication infrastructures such as routers, leased lines, MPLS networks, or the public internet. Data transmitted will travel through these communication paths before reaching its destination.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how WAN works:
WAN comes in multiple forms. Here are some of the most common:
WAN plays a vital role in supporting modern operations. Some of its key benefits include:
Businesses can connect headquarters, branches, warehouses, and partners into one unified network.
Employees across different locations can access company applications, files, and databases in real-time.
WAN enables secure and consistent access to central data centers as well as cloud-based applications.
Companies can easily add new branches without rebuilding networking systems from scratch.
Highly relevant for global organizations operating in multiple regions.
Despite its many advantages, conventional WAN also faces some difficulties:
These limitations accelerate the rise of SD-WAN — offering automation, flexibility, and far better cost efficiency. If traditional WAN is the foundation, then SD-WAN is its smart evolution.
WAN (Wide Area Network) is a core networking technology that enables connectivity across company branches in various geographic locations. With WAN, business integration across cities or even countries becomes easier, although challenges such as high costs and complex management remain.
Data center is a complex ecosystem. It houses hundreds to thousands of servers, networking devices, cooling systems, and power units, all of which must work in unison without interruption. Managing all these components manually is nearly impossible. This is why advanced management technology is crucial, not just for the data center operators, but for you as the client.
One of the most critical technologies in modern data center management is DCIM, or Data Center Infrastructure Management. But what exactly is DCIM, and more importantly, how does this technology provide direct benefits to you when using colocation services?
Simply put, DCIM (Data Center Infrastructure Management) is a centralized software solution used to monitor, measure, manage, and optimize all the physical infrastructure within a data center. Think of DCIM as a “digital control panel” that provides a comprehensive overview of everything happening inside the facility, from individual server racks to large-scale cooling systems.
The core functions of a DCIM system include:
Although DCIM is a tool operated by the data center provider, its benefits extend directly to you as a client entrusting them with your critical IT assets. Here are the five main advantages you gain:
In the past, you might have needed to make a physical visit to know the exact condition of your servers in a colocation facility. With DCIM, transparency is significantly enhanced. Many modern data center providers, including EDGE DC, offer a customer portal that integrates with their DCIM system.
Through this portal, you can gain complete visibility into your environment remotely, allowing you to:
This transparency provides peace of mind, as you know exactly what is happening with your infrastructure at all times.
DCIM transforms operational data into actionable insights. As a client, you can leverage this data to make strategic decisions regarding your IT infrastructure.
For instance, with power consumption data from DCIM, you can:
This helps you manage scalability and business growth more effectively and with a data-backed approach.
One of the greatest benefits of DCIM is its ability to detect potential issues before they become major disruptions. The DCIM system proactively monitors every critical data center component.
If an anomaly occurs—such as a rack temperature beginning to rise or an unusual power spike—the system automatically sends an alert to the data center’s operations team. This rapid response enables them to take preventive action, thereby preventing downtime that could harm your business. This higher reliability directly impacts the continuity of your digital services.
Many companies now have Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) or sustainability targets. Choosing the right data center partner can help you achieve these goals. DCIM plays a key role in the operation of a Green Data Center.
By continuously monitoring and optimizing energy usage, data centers can reduce their carbon footprint. For you as a client, this means your infrastructure is hosted in an efficient and environmentally responsible facility, aligning with your company’s values.
For your IT team, DCIM simplifies many management tasks. Through the customer portal, you can not only monitor but also request services more easily. For example, if you need on-site technical assistance (a “remote hands” service), you can raise a ticket directly through the integrated portal.
This saves time and resources, allowing your team to focus on other strategic tasks rather than operational logistics.
Ultimately, the implementation of DCIM by a data center provider reflects their commitment to operational excellence, transparency, and reliability. This technology is no longer just a “nice-to-have” feature; it is a fundamental component of a reliable data center service.
As a client, the benefits of DCIM give you greater control, deeper insights, and the confidence that your digital assets are in the right hands. With an infrastructure that is proactively monitored and managed, you can focus more on driving your business’s innovation and growth.
Interested in learning more about how EDGE DC leverages advanced technologies like DCIM to deliver best-in-class services for your digital infrastructure? Contact our team today to find the right solution for your business needs.